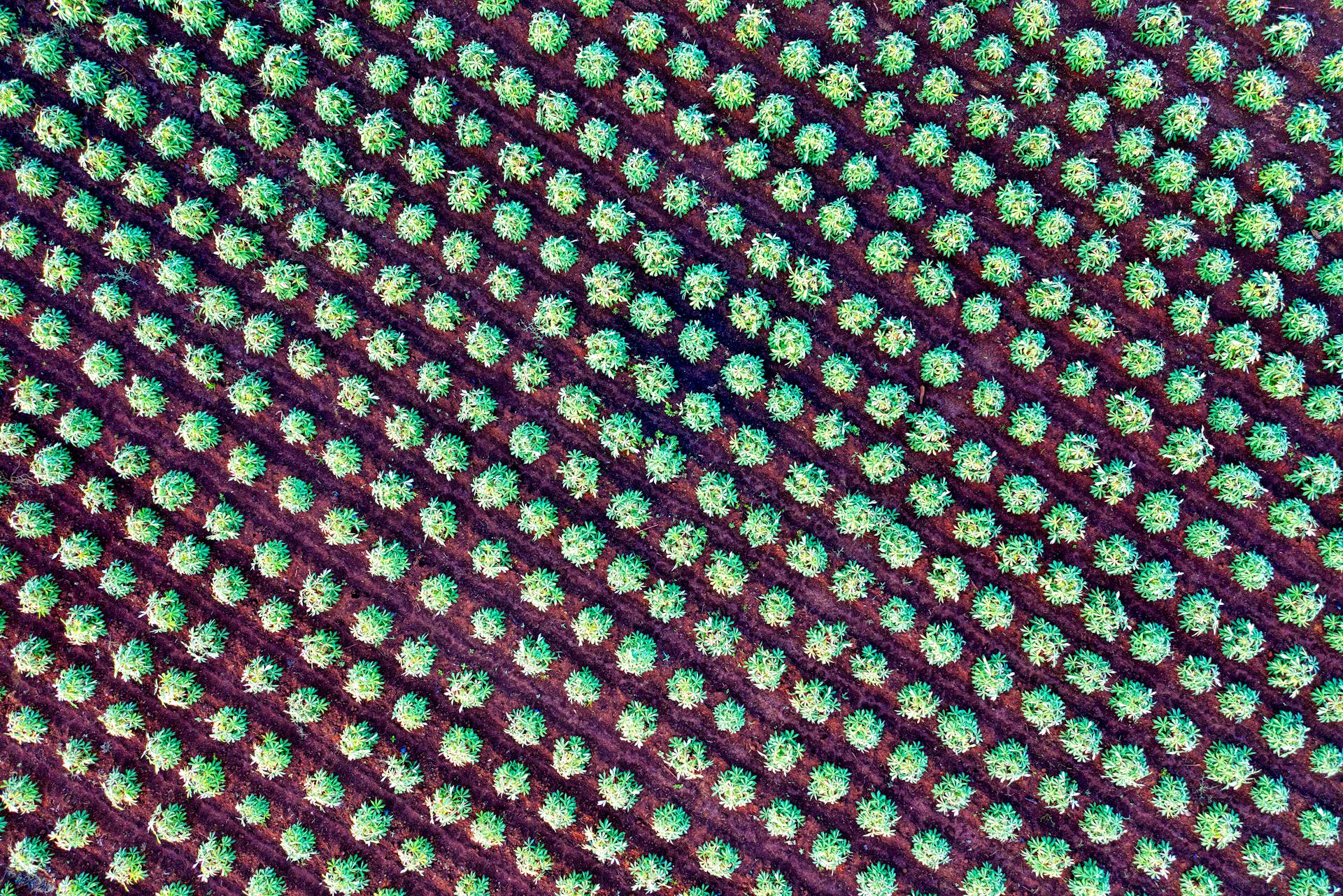
Drones are revolutionizing the way farmers work, providing a bird's-eye view of their fields like never before.
Aerial monitoring allows farmers to detect issues such as crop stress, disease, and pests early on, reducing the need for costly chemical treatments and preserving the environment.
With drones, farmers can also create detailed maps of their fields, helping them optimize crop yields and reduce waste.
Precision farming is becoming increasingly popular, and drones are at the forefront of this movement, enabling farmers to apply the right amount of water, fertilizer, and pesticides exactly where they're needed.
Drones are also being used to inspect irrigation systems, detect leaks, and optimize water usage, helping farmers conserve this precious resource.
By leveraging drone technology, farmers can increase their productivity, reduce costs, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Drones for Farming Operations
Drones equipped with Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) imaging can indicate plant health, allowing farmers to monitor crops and address problems promptly.
Drones can fly close to fields, reducing the impact of cloud cover and poor light conditions, and providing accurate image location to the millimeter.
Many farmers already use satellite imagery to monitor crop growth, but drone imaging is often more effective and cost-efficient.
With drones, farmers can cover hundreds of hectares in a single flight, capturing data that helps detect and identify crop stress and variability.
Drones can also be equipped with regular cameras to quickly evaluate damage after a storm or inspect fences for damage, saving farmers time and effort.
Scouting/Monitoring Plant Health
Scouting/Monitoring Plant Health is one of the most exciting uses of drones in farming operations. Drones equipped with special imaging equipment called Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) can indicate plant health by using detailed color information.
This allows farmers to monitor crops as they grow, detecting any problems early on and saving the plants. Farmers can also use drones with regular cameras to monitor crop health, which is more cost-effective and accurate than satellite imagery.
With drones, farmers can spot areas with stand gaps and replant as needed, and detect disease or pest problems early on. This proactive approach leads to higher-quality crops and sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
Drones can also provide accurate field mapping, including elevation information, to help growers identify irregularities in the field. This information is useful for determining drainage patterns and wet/dry spots, allowing for more efficient watering techniques.
Here are some key benefits of using drones for scouting/monitoring plant health:
- Early detection of problems saves plants and reduces crop losses
- Cost-effective and accurate alternative to satellite imagery
- Accurate field mapping and elevation information for efficient watering techniques
- Proactive approach leads to higher-quality crops and sustainable agricultural ecosystems
Overall, drones are revolutionizing the way farmers scout and monitor plant health, making it easier to grow high-quality crops while reducing waste and environmental impact.
Planting and Seeding
Drones are being used for planting seeds in forestry industries, particularly in hard-to-reach areas where workers might be endangered.
Automated drone seeders can plant much more efficiently than traditional methods, with a team of two operators and ten drones capable of planting 400,000 trees in a day.
Livestock Tracking
Livestock tracking is a fascinating application of drone technology in farming. Drones can track animal movements and monitor health through aerial counts or thermal imaging.
Professionals have been using drones for livestock tracking, especially in areas where tracking devices can be difficult to place on large animals. A notable example is the University of North Dakota, where a biology professor used drones to track bison in the Theodore Roosevelt National Park in 2019.
Drones offer a safer and more efficient way to track livestock, eliminating the need for manual tracking devices that can be hazardous for humans. This technology has the potential to revolutionize livestock management and improve animal welfare.
The University of North Dakota's experience with tracking bison using drones demonstrates the effectiveness of this approach. By leveraging drone technology, farmers can gain valuable insights into their livestock's behavior and health, enabling them to make informed decisions about their operations.
Regulating Operations
Regulating operations is crucial for a successful drone farming operation. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates drone flying, and the type of certification needed is based on how the drone is being used.
To fly a drone, you need to obtain a certificate from the FAA, and the requirements are fact-specific. The type of certification needed depends on the intended use of the drone, where it's being flown, and other factors.
Flying a drone requires safe height and awareness of potential obstructions in the flight path. It's essential to know and follow regulations to avoid any issues.
The FAA has promulgated a number of regulations, and Part 107 is one of the main provisions. Part 107 is housed within Title 14 Subchapter F within the Code of Federal Regulations.
Regulations can be complex, but a good starting point is to understand the basics of Part 107. This will give you a solid foundation for your drone operations.
Recreational vs. Commercial Use
If you plan to use a drone for commercial purposes like agricultural operations, you'll need to get certified under Part 107.
To acquire this certification, you must be at least 16 years old.
You'll also need to be able to read, write, and understand English.
Additionally, you must be in a physical and mental condition to safely fly a drone.
To get certified, you'll need to take a knowledge test created by the FAA at an approved test center.
The test will cover general flight basics and restrictions, as well as questions specific to drone operation.
If you're already a pilot with a Part 61 Certification and have completed a flight review within the past 24 months, you can opt to take an online training course through the FAA Safety Team Website instead.
Drones for Farming Efficiency
Drones can be equipped with sophisticated programming that detects and records variations in plant numbers, health, height, and other statistics.
This data helps farmers identify trouble spots in their fields and focus their time and resources accordingly.
Producers can guide the controls of the drones themselves, but software also exists that can guide the drones on a pre-programmed flight over the field.
Drones can maintain a preset height over the plants, compensating for changes in terrain while scanning the plants as they fly overhead.
By using drones, farmers can quickly identify areas of poor drainage or less-than-ideal soil conditions in their fields.
Drones for Farming Data
Drones equipped with multispectral sensors can direct you to the best places to sample for soil and leaf sampling, saving time and money. This is especially useful for farmers who want to optimize their treatments and reduce costs.
High-resolution data is a key advantage of using drones for farming. With resolutions down to 1.3 inches per pixel, drones can capture plant variability at a per-plant level or empower plant counting at earlier stages of growth.
Drones can achieve a staggering 1.2cm full-color sharpened ground resolution at an altitude of 60m, making them ideal for precise data collection and vegetation analysis.
Regularly tracking crops over time is crucial for research or production. Drones can capture periodic data from professional multispectral sensors, offering insights into crop health regardless of illumination changes.
Crop damage assessment and documentation can be done using drone data, providing critical information for measuring and documenting damage caused by floods, fire, pests, weather events, etc.
Precision agriculture drones can detect and record variations in plant numbers, health, height, and other statistics. This data can help farmers quickly identify trouble spots where they need to focus their time and resources.
Here are some of the key sensors used in agriculture drones:
- Cameras: capable of capturing high-resolution images and include RGB (visible light), multispectral, or thermal imaging sensors
- LiDAR sensors: create detailed 3D maps of the terrain
- Infrared sensors: monitor crop health, identify stress in plants, and detect temperature
- Ultrasonic sensors: help drones maintain a consistent altitude above the ground
These sensors empower farmers with intricate insights into topographical variations, soil composition, and drainage patterns across their fields.
Drones for Farming Management
Drones for Farming Management are a game-changer for farmers. They can be guided by specialized software programs that work in conjunction with GPS and GIS.
These programs allow drones to fly over fields and provide detailed information on crop health, growth, and density. This is especially useful for monitoring plant health, as drones can detect subtle variations in plant stress, nutrient deficiencies, or diseases.
Drones equipped with NDVI imaging can indicate plant health by using detailed colour information. This allows farmers to quickly identify and address any problems before it's too late.
Other Certifications & Requirements
If you plan to use drones for aerial applications, you'll need to obtain a certificate under Part 137. This certification is specific to using drones to dispense substances like pesticides or disinfectants.
In North Dakota, drone applicators must meet certain safety requirements and receive licensing from the ND Aeronautics Commission. This ensures that drone operations are carried out safely and responsibly.
Flying a drone requires a certificate from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), which is based on how the drone is being used and where it's being flown.
Livestock Management and Health
Drones play a crucial role in livestock management by monitoring livestock health and tracking animal movements.
Professionals use drones to assess pasture conditions, which is a key aspect of integrated farming practices.
Drones allow for aerial counts of livestock, making it possible to track large numbers of animals without having to physically count them.
A UND biology professor used drones to track bison in the Theodore Roosevelt National Park, demonstrating the effectiveness of this technology.
Thermal imaging can be used with drones to track livestock, especially in situations where traditional methods are not feasible.
This approach to livestock management is not only efficient but also helps ensure the well-being of both crops and livestock.
Additional reading: Drones in Wildfire Management
Benefits and Advantages
Using drones in agriculture offers several benefits and advantages. One of the main advantages is the speed at which data can be collected.
Drones can quickly zero in on smaller problem areas, allowing producers to take steps to rectify any problems and move on to the next field without needing heavy equipment.
Drones are designed to be extremely precise and don't damage plants or disturb soil in the field.
In Nebraska, drones are being used to map fields and assess plant condition, showing their potential for agricultural use.
Precise application of chemicals is another way drones are being used in agriculture, allowing for targeted and efficient use of resources.
You might enjoy: Use of UAVs in Law Enforcement
Frequently Asked Questions
How are agricultural drones different from other drones?
Agricultural drones are unique in their ability to provide detailed insights into soil composition, topography, and drainage patterns through advanced sensors and high-resolution cameras. This specialized technology sets them apart from other drones, making them a valuable tool for precision farming.
Sources
- https://www.croptracker.com/blog/drone-technology-in-agriculture.html
- https://futurefarmermag.com/how-drones-are-transforming-the-future-of-farming/
- https://wingtra.com/drone-mapping-applications/use-of-drones-in-agriculture/
- https://www.jouav.com/blog/agriculture-drone.html
- https://nebraskacorn.gov/cornstalk/sustainability/four-ways-drones-are-used-in-agriculture/
Featured Images: pexels.com